Precision Oncology
Precision oncology is revolutionizing cancer treatment by tailoring therapies to the genetic profile of each patient’s tumor. This innovative approach involves identifying genetic mutations and alterations that drive cancer growth and developing targeted treatments that are more effective and less harmful than traditional therapies.
MACS Clinic a highly respected center for cancer treatment in Bangalore, explains, “Precision oncology aims to improve outcomes and offer hope to patients with even the most challenging diagnoses by focusing on the specific characteristics of each cancer.”
With extensive experience and expertise in cancer surgery and precision oncology, MACS Clinic is dedicated to providing cutting-edge treatments to its patients. His commitment to personalized care ensures that each patient receives a treatment plan tailored to their unique genetic makeup, offering the best possible chance for a successful outcome.
Let’s delve deeper into this advanced approach to cancer treatment.

What is Precision Oncology?
Precision oncology, also known as personalized or individualized oncology, is defined as molecular profiling of tumors to identify targetable alterations. It focuses on using genetic information to guide cancer treatment.
Unlike traditional approaches that treat cancer based on its location in the body, precision oncology targets the specific genetic mutations causing cancer cell growth. This approach leads to more precise and effective treatments, reducing side effects and improving patient outcomes. It is particularly beneficial for patients with advanced cancers or those who have not responded to standard therapies.
Transform your cancer treatment experience. Consult a seasoned oncologist to learn more about precision oncology.
Want to understand how precision oncology actually works? Let’s find out.
How Does Precision Oncology Work?
The goal of precision medicine is to deliver the right cancer treatment to the right patient at the right dose and the right time. Precision oncology begins with a thorough analysis of the patient’s cancer cells. This typically involves genomic sequencing that identifies the specific genetic mutations and alterations in the tumor. Once this information is obtained, a tailored treatment plan is developed to target the particular abnormalities.
MACS Clinic states, “The process of precision oncology is highly detailed and involves a multidisciplinary team. We gather extensive data on the tumor’s genetic profile. This helps us design the most effective treatment strategy for each patient.”
This approach allows for more targeted therapies and helps monitor treatment efficacy. As the patient’s treatment progresses, ongoing genomic testing can identify any new mutations or changes in the tumor. It helps make any required modifications to the treatment plan, ensuring the treatment remains effective over time.
Let’s take a closer look at the steps involved in precision oncology and its key objectives.

Fill Out the Form Below
Is Precision Oncology of Any Use in Cancer Treatment as of Now?
Precision oncology is making significant strides in cancer treatment. By tailoring therapies to the individual characteristics of each patient’s tumor, it has shown promising results in various types of cancer. Patients undergoing precision oncology often experience better outcomes, including improved survival rates and quality of life.
MACS Clinic states that, “Precision oncology is not just a future promise; it is already transforming cancer care. Patients receive more personalized and effective treatments, leading to better results. This approach is particularly beneficial for those with rare or difficult-to-treat cancers, where traditional methods may fall short.”
Here are a few examples of the use of precision oncology:


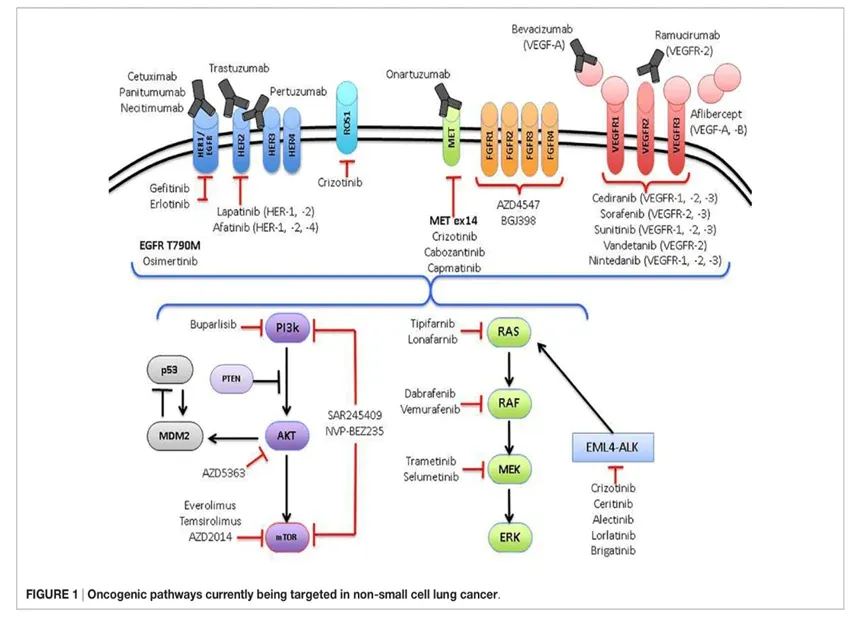
The Primary Objectives of the Precision Oncology Clinic Are:
a. Data Gathering:
A detailed history and physical examination are needed to understand the case in depth. All available investigations, including scans, histopathology, previous genomic tests, if available, and other relevant investigations, will be reviewed.
b. Testing:
The main idea is to conduct comprehensive genomic tests of the tumor tissue or patient’s blood to look for biomarkers in the tumor sample and develop enhanced patient treatment strategies for improved outcomes.
A detailed genomic analysis will provide information about:
- The DNA sequence
- Structural variation
- Gene expression or the specific gene mutation
These details will provide the basis for personalized treatment of the patient.
c. Molecular Tumor Board:
Here, medical oncologists, pathologists, and molecular oncologists collaborate to present clinical cases, along with pathological and molecular data to identify novel therapeutic strategies for personalized treatment plans.
d. Recommendations:
There are cancer-specific standard-of-care guidelines that include single or multimodality treatment, such as:
- Surgery
- Radiation
- Chemotherapy
- Targeted therapy
- Immunotherapy
Based on the tumor type and standard of care, biomarker-specific personalized treatment plans will be made after an in-depth and comprehensive case review.
Conclusion
Benefits:
– Improved response rates and survival for patients with actionable mutations.
– Reduced side effects compared to traditional chemotherapy.
Challenges:
– Not all tumors have targetable mutations.
– Resistance to therapy can develop.
– High cost of NGS testing and targeted therapies.
– Limited access to clinical trials for some patients.
Future Directions:
– Development of new targeted therapies for a wider range of mutations.
– Tumor-agnostic therapies are effective across multiple cancer types.
– Improved methods to overcome resistance.
– Increased access to NGS testing and precision oncology treatments.

