Why Awareness Matters
“Awareness is the first step towards prevention and timely intervention. Esophageal cancer often goes unnoticed until it’s advanced. Spreading knowledge could save lives,” explains Dr. Sandeep Nayak, a senior surgical oncologist at MACS Clinic, Bangalore.
April is Esophageal Cancer Awareness Month, a crucial time dedicated to raising awareness about this silent yet deadly cancer. Knowing the signs, being aware of the risk factors, and recognizing when to get help can be the difference between life and death.
What is Esophageal Cancer?
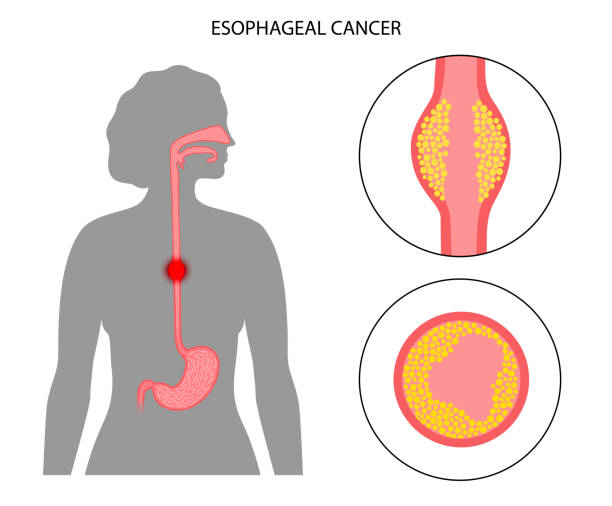
Esophageal cancer begins in the esophagus—the long, hollow tube that connects the throat to the stomach. Its primary function is to carry food and liquids into the digestive system. The disease usually starts in the cells lining the esophagus and can grow silently, often showing symptoms only in the later stages.
There are two major types of esophageal cancer:
Adenocarcinoma: More common in the lower esophagus, particularly in individuals with chronic acid reflux.
Squamous cell carcinoma: More common in the upper and middle esophagus, frequently associated with smoking and alcohol use.
Both are serious, but with early diagnosis and treatment, outcome can be improved.
Knowing the potential warning signs is of great help.
Signs and Symptoms to Recognize Early

| Symptom | Explanation |
| Difficulty swallowing | Generally, the first sign, as tumor growth narrows the esophagus |
| Unintended weight loss | May be due to eating difficulty or metabolic changes in the body |
| Chest pain or discomfort | Can be caused by pressure or irritation in the esophagus |
| Persistent cough or hoarseness | Especially if the cancer is near the voice box or affects nerves |
| Indigestion or heartburn | Frequent and severe bouts could mean underlying issues |
| Vomiting or regurgitation | As food passage is blocked, vomiting may occur |
Read on to know the risk factor.
Who is at Risk? Key Risk Factors

Some lifestyle habits, illnesses, and hereditary factors can raise the risk of esophageal cancer. These are:
Chronic acid reflux or GERD: Esophageal lining is damaged by long-term acid exposure.
Barrett’s esophagus: A condition where esophageal lining changes, usually as a result of GERD.
Tobacco and alcohol consumption: Both are major factors, particularly when combined.
Obesity: It increases acid reflux and inflammation.
Age and gender: More prevalent in men aged over 50.
Diet lacking fruits and vegetables: Inadequate protective nutrients may play a part.
Here’s how to reduce your risks.
How to Prevent Esophageal Cancer

Stop smoking and reduce alcohol intake: These are two of the most effective measures.
Manage acid reflux: Treatment of GERD early on can avoid transition to Barrett’s esophagus.
Keep a healthy weight: Regular physical activity and a balanced diet keep acid levels under control.
Follow a healthy diet: Have lots of fruits, vegetables, and whole grain.
Undergo regular screening: If you have high risk factors, particularly if you are diagnosed with Barrett’s esophagus.
Check out the tests and scans that help detect esophageal cancer.
Diagnosis: How Esophageal Cancer is Detected

Early diagnosis commonly begins with a thorough evaluation of symptoms, followed by imaging and biopsy procedures:
- Endoscopy: A tube with a camera examines the esophagus for abnormal growths.
- Biopsy: Samples of tissue are removed during endoscopy to verify cancer cells.
- CT scan or PET scan: Assists in determining the stage and extent of the disease.
Prompt and accurate diagnosis is necessary for choosing the optimal treatment course.
Now, let’s understand the treatment options for esophageal cancer.
Treatment Options: What Happens Next?
Surgery: Removal of part or all of the esophagus may be necessary in early or localized cancers.
Radiation therapy: High-energy rays target and destroy cancer cells.
Chemotherapy: Drugs used to kill cancer cells, often in combination with radiation.
Targeted therapy and immunotherapy: For advanced cases, newer treatments are used to target distinctive mechanisms of cancer cells or enhance the body’s immune response.
Palliative care: Seeks to alleviate symptoms and enhance quality of life, particularly in the late stages.
At MACS Clinic Bangalore, the latest and minimally invasive procedures like robotic-assisted and laparoscopic surgeries are provided, which help in quicker recovery, less pain, and more precision in surgery. A multidisciplinary approach ensures end-to-end care, bringing together medical expertise and patient-oriented planning.
Conclusion
Frequently Asked Questions
Is esophageal cancer common?
Esophageal cancer is not as common but has a high mortality rate owing to late diagnosis. It is one of the top ten causes of cancer death worldwide.
What's the difference between GERD and esophageal cancer?
GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease) is a chronic illness in which stomach acid backflows into the esophagus. Although not cancer, if left untreated, GERD can progress to Barrett’s esophagus, increasing cancer risk.
Can young adults get esophageal cancer?
While uncommon, young adults can develop esophageal cancer, particularly with underlying factors such as genetic disorders, severe GERD, or prolonged exposure to tobacco.
Where can I find more information?
For further information regarding symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options, visit our page on esophageal cancer.
What color represents Esophageal Cancer Awareness?
The official Esophageal Cancer Awareness color is periwinkle blue, representing hope and awareness for victims of the disease.
Disclaimer: The information shared in this content is for educational purposes and not promotional.

